Introduction: The Indispensable Navigator of the Search Landscape
In the highly competitive and constantly evolving arena of Search Engine Optimization (SEO), digital marketers, content strategists, and business owners require tools that can provide deep, actionable insights into the web’s structure and dynamics. Among these essential tools, Ahrefs stands out not merely as a utility, but as a foundational ecosystem for data-driven SEO strategy.
Ahrefs began its journey primarily as a sophisticated backlink analysis tool, swiftly gaining reputation for the size and accuracy of its web crawl and index. Today, it has evolved into a comprehensive SEO suite, housing a powerful array of tools including Site Explorer, Keywords Explorer, Content Explorer, Site Audit, and Rank Tracker. These tools collectively offer a 360-degree view of the competitive landscape, technical health, content opportunities, and link profile of any website.
The request for a 3,000-word analysis allows for a deep examination of the platform, detailing its core technical infrastructure, dissecting the functionality of its key modules, scrutinizing its proprietary metrics, and illustrating its indispensable role in modern digital strategy. This essay argues that Ahrefs’ success lies in its unparalleled data quality, its user-centric design, and its ability to transform complex, raw web data into clear, strategic intelligence.
Part I: The Technological Foundation—The AhrefsBot and the Data Index
The foundation of Ahrefs’ power is its vast and continually updated proprietary data. Unlike many competitors who may rely on third-party data or smaller sampling, Ahrefs has invested heavily in creating its own web crawler, the AhrefsBot.
1. The Scale of the Crawl
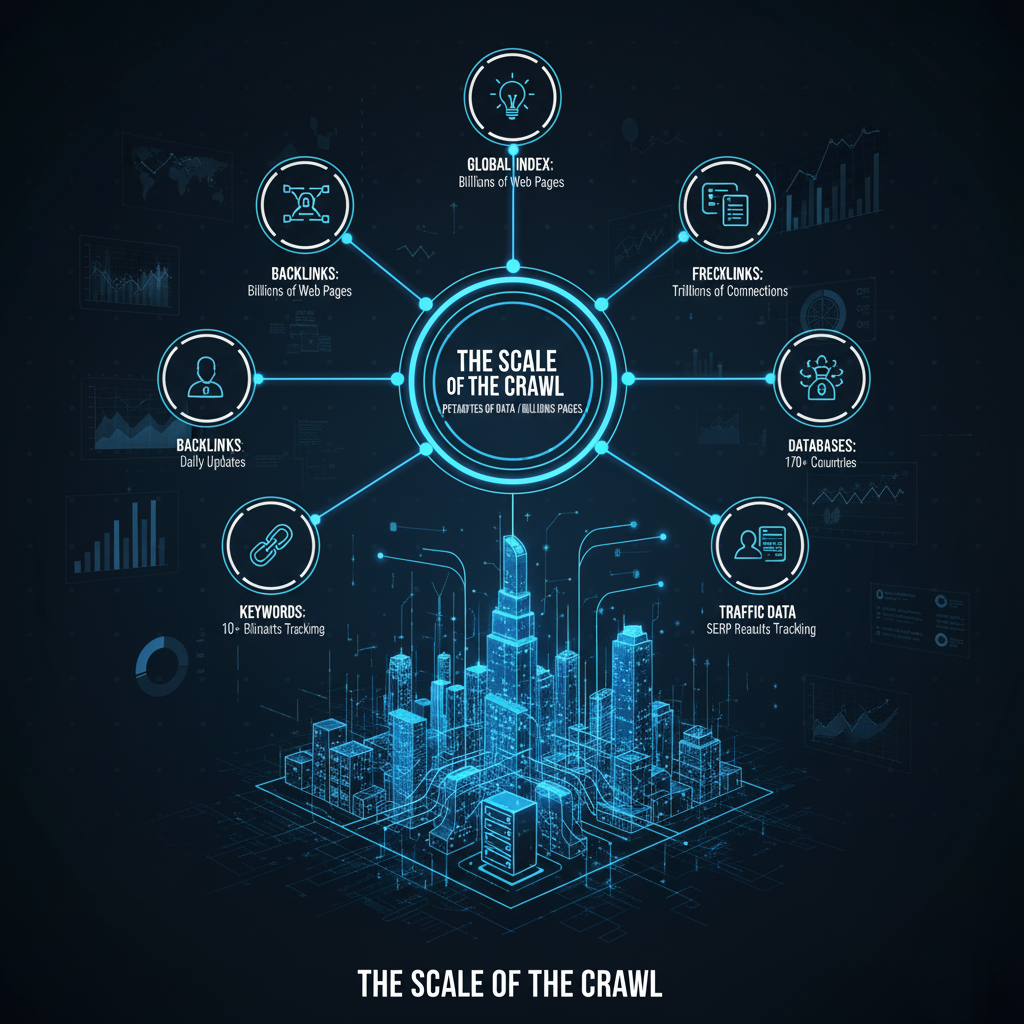
The AhrefsBot is one of the most active web crawlers in the world, second only to Google’s own search bots. Its mission is to index the entire public web, focusing specifically on collecting two critical categories of data:
- Link Data: This includes identifying every single hyperlink between every page, recording the anchor text used, the link type (dofollow, nofollow, sponsored, UGC), and the context of the link. As of recent estimates, Ahrefs’ backlink index contains trillions of pages and petabytes of data, making it the most authoritative source for link graph analysis outside of Google.
- Keyword and SERP Data: The bot continuously crawls the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) across numerous countries and languages, tracking the top 100 results for billions of keywords. This allows Ahrefs to map which websites rank for which queries, and critically, how often users actually click on those results.
2. The Data Index and Infrastructure
Maintaining this massive index requires formidable infrastructure and engineering excellence. The data is not static; links break, pages are updated, and rankings fluctuate constantly. Ahrefs employs sophisticated indexing technologies to update its database every 15 to 30 minutes, providing marketers with near real-time insights—a crucial advantage in fast-moving industries.
This proprietary database is the central truth for all of Ahrefs’ tools. Without this high-quality, high-velocity data, the subsequent analytical tools would be rendered useless. It is this infrastructure investment that provides Ahrefs with its primary competitive moat.
Part II: Dissecting the Five Core Tools
The Ahrefs platform is organized around five main tools, each serving a distinct and critical function in the SEO workflow.
1. Site Explorer: The Competitive Intelligence Hub
Site Explorer is the most used tool in the Ahrefs suite and serves as a digital marketer’s competitive intelligence engine. By inputting a domain, users gain immediate access to comprehensive data across three primary analysis pillars:
- Backlink Analysis: This is Ahrefs’ historical strength. Users can see every domain linking to a site (Referring Domains), the quality and quantity of those links, the growth rate of the link profile, and the anchor text distribution. Crucially, it allows for the identification of toxic or low-quality links that may warrant disavowal.
- Organic Traffic Research: Site Explorer estimates a website’s organic search traffic volume and the monetary value of that traffic. It lists the exact keywords driving traffic, the landing pages that receive the most visibility, and the historical trend of traffic growth or decline. This allows marketers to quickly benchmark themselves against competitors.
- Paid Traffic Research: The tool also provides insights into paid search activities (PPC), showing which keywords a competitor is bidding on, their ad copy, and their most effective landing pages. This capability provides a comprehensive view of a competitor’s digital marketing spend and strategy.
2. Keywords Explorer: Uncovering Search Demand
Keywords Explorer is the foundation of content strategy and optimization, designed to understand user intent and search demand.
- Keyword Metrics: It provides essential metrics for any search query, including:
- Search Volume: Estimated monthly searches.
- Keyword Difficulty (KD): A proprietary metric estimating how hard it is to rank in the top 10 results, based primarily on the number of linking websites required.
- Clicks: A critical differentiator. Ahrefs estimates the actual number of clicks a SERP receives, factoring in zero-click searches (where the answer is found directly in the SERP feature). This ensures marketers prioritize keywords that actually drive traffic.
- SERP Analysis and Parent Topic: The tool shows the current top 10 results for any keyword, detailing their Domain Rating and Backlink profile. It also identifies the “Parent Topic”—the broader subject under which the keyword naturally falls—helping users to build topical authority rather than optimizing for narrow, isolated terms.
3. Content Explorer: The Ideation Machine
Content Explorer acts as a searchable database of billions of web pages, enabling marketers to find the most popular and link-worthy content on any topic.
- Filtering by Performance: Users can search for content based on keywords and then filter by critical performance indicators, such as:
- Organic Traffic: Finding content that is successfully generating search traffic.
- Referring Domains: Identifying articles that have earned the most backlinks (demonstrating link-worthiness).
- Social Shares: Gauging social media popularity.
- Strategic Utility: This tool is invaluable for competitive content gap analysis, finding successful content formats, and discovering broken or outdated pages that are ripe for the Skyscraper Technique (a link-building strategy).
4. Site Audit: The Technical SEO Diagnostic
While the other tools focus on external competitive analysis, Site Audit focuses inward, functioning as an essential technical SEO health check.
- Comprehensive Crawl: The tool crawls a user’s entire website, checking every page against over 100 pre-defined SEO parameters.
- Reporting and Prioritization: It generates detailed reports categorizing issues such as: broken links (4xx errors), server errors (5xx errors), slow pages, missing alt text, duplicate content, correct use of robots.txt and sitemap files, and proper implementation of Hreflang and canonical tags. The system intelligently groups and prioritizes these issues based on severity, allowing developers and SEOs to focus on fixes that yield the greatest impact.
5. Rank Tracker: The Performance Monitor
Rank Tracker provides the essential function of monitoring a website’s visibility over time for a curated list of keywords.
- Visibility Metrics: Users track their rankings across various locations and devices (desktop/mobile). The tool calculates key performance indicators (KPIs) like Visibility (the percentage of clicks a site receives from tracked keywords) and Average Position, making it easy to report progress to stakeholders.
- SERP Feature Tracking: It tracks whether a website is capturing valuable SERP features like Featured Snippets, knowledge panels, and image packs, which often drive disproportionately high click-through rates.
Part III: The Power of Proprietary Metrics
Ahrefs’ proprietary metrics are widely adopted industry standards that simplify the complexity of SEO into digestible, comparative scores. Understanding these metrics is key to interpreting Ahrefs’ data.
1. Domain Rating (DR)
Domain Rating is arguably Ahrefs’ most recognized metric. It represents the strength of a website’s overall backlink profile on a logarithmic scale from 0 to 100.
- How it Works: DR is calculated based on the quality and quantity of backlinks pointing to the domain. Crucially, it takes into account the DR of the linking domains themselves. Receiving a link from a high-DR site (like a major news publication) is far more impactful than receiving hundreds of links from low-DR sites.
- Strategic Use: DR is used primarily for competitive benchmarking and link prospecting. A marketer will target acquiring links from sites with a DR equal to or higher than their own, and they use a competitor’s DR to gauge the difficulty of overtaking them in the SERPs.
2. URL Rating (UR)
URL Rating is similar to DR but measures the strength of a specific page or URL. It measures the quality of the backlink profile pointing directly to that page.
- Distinction from DR: A site’s Domain Rating (DR) is high because of its overall link profile, but a specific URL on that site might have a low URL Rating (UR) if it hasn’t attracted many links itself. This metric helps in internal linking strategy, ensuring that high-UR pages pass their authority to other important pages on the site.
3. Ahrefs Rank (AR)
Ahrefs Rank is essentially a reverse-ranking of all websites in the Ahrefs index based on their Domain Rating. The site with the highest DR (usually Google or Facebook) holds Ahrefs Rank #1.
- Purpose: While DR is a score, AR provides a rank. It is primarily used to observe the trend of a site’s growth relative to the rest of the web. Moving from AR 1,000,000 to AR 100,000 indicates massive growth in authority, even if the DR score only changes slightly due to the logarithmic scale.
Part IV: Strategic Applications in Modern Marketing
The true value of Ahrefs lies not in its data, but in how practitioners use that data to formulate winning digital strategies.
1. Advanced Competitive Link Analysis
Ahrefs enables “peeking behind the curtain” of successful competitors.
- Link Intersect: This feature identifies websites that link to multiple competitors but not to the user’s site. These are prime targets for link outreach, as they have already demonstrated an affinity for the niche content.
- Broken Link Building: Marketers use Site Explorer to find broken outbound links on high-authority sites. They then create superior content to replace the dead page and suggest it to the linking site’s owner, simultaneously earning a valuable backlink and improving the quality of the internet.
2. Content Gap Analysis and Topic Clustering
Keywords Explorer is the foundation for filling content gaps.
- Gap Analysis: By comparing the user’s site against 2-3 top competitors, the tool reveals keywords for which the competitors rank highly, but the user’s site does not rank at all. These missing keywords represent immediate content opportunities.
- Pillar and Cluster Strategy: The Parent Topic feature encourages the creation of “Pillar Pages” (broad, authoritative content) supported by “Cluster Content” (detailed, specific articles). Ahrefs helps map this entire structure by identifying all related sub-topics and their respective keyword difficulty scores.
3. Monitoring and Risk Mitigation
The platform plays a crucial defensive role by continuously monitoring the website.
- Security Alerts: Ahrefs can alert a user when a sudden, massive influx of suspicious links occurs, which may signal a negative SEO attack. This allows for rapid disavowal and mitigation before Google penalizes the site.
- Tracking Site Migration: When a website undergoes a technical migration (e.g., from HTTP to HTTPS or an architectural change), the Site Audit tool is indispensable for ensuring all redirects (301s) are correctly implemented and no SEO value (link equity) is lost.
Part V: Market Position and Future Trajectory
Ahrefs operates in a competitive market dominated by a few major players. Its market strategy focuses heavily on data quality, speed, and integrated utility.
1. Competitive Landscape
Ahrefs’ primary competitors include SEMrush, Moz, and Majestic.
- Ahrefs vs. SEMrush: Ahrefs is generally considered the industry leader in backlink depth and quality, while SEMrush is often preferred for its broader suite of non-SEO marketing tools (e.g., social media, content marketing, advertising features).
- Ahrefs vs. Moz: Moz relies on its proprietary Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA) metrics, which, while similar to DR and UR, are calculated differently. Ahrefs often boasts a faster crawl and a larger index.
2. Commitment to Content and Education
A significant part of the Ahrefs brand strategy is its commitment to education. Its blog is renowned for publishing high-quality, data-driven SEO tutorials and case studies, often featuring their own tools in practical workflows. This strategy creates a cycle where the tool itself is promoted through genuinely valuable educational content, fostering user loyalty and industry trust.
3. The Future of Ahrefs
The future evolution of Ahrefs will likely focus on three areas:
- AI Integration: Leveraging AI to interpret user intent in Keywords Explorer more accurately, and integrating large language models to provide AI-generated content outlines or on-page optimization suggestions directly within the Site Audit reports.
- SERP Feature Expansion: Continually tracking and interpreting the impact of new SERP features like generative AI answers, video carousels, and image packs, which constantly change how organic clicks are distributed.
- Local SEO Depth: Enhancing its capability for hyper-local keyword tracking and audit features to better serve brick-and-mortar businesses and local SEO practitioners.
Conclusion
Ahrefs is not merely an SEO tool; it is a vital lens through which the complexity of the modern web is brought into focus. From the relentless crawling of the AhrefsBot to the actionable intelligence provided by Site Explorer and Keywords Explorer, the platform has established itself as the indispensable engine of data-driven SEO.
Its success is rooted in an unwavering commitment to the scale and accuracy of its proprietary data, transformed into intuitive metrics like Domain Rating that simplify complex decision-making. For any individual or organization serious about competing for visibility in search, mastering Ahrefs is synonymous with mastering the art and science of SEO itself. As search engine algorithms continue to evolve, Ahrefs remains the central navigational instrument, guiding marketers through the ever-changing tides of the digital landscape.